The concept of gravitational force is a fundamental aspect of physics that governs the interactions between objects with mass. Understanding what affects this force can illuminate various phenomena, from the falling of an apple to the Earth to the orbits of planets around the sun. One critical question arises: which change will always result in an increase in the gravitational force? This inquiry invites us to explore the principles of gravity, the masses involved, and the distances separating these masses. By delving into this topic, we can better comprehend the nature of gravitational interactions.
Gravitational force is not merely an abstract concept; it has real-world implications and applications that affect our daily lives and the universe as a whole. The force of gravity is responsible for keeping us anchored to the ground, influencing the tides, and governing the movements of celestial bodies. To fully grasp the dynamics of gravity, we must analyze the factors that contribute to its strength and how alterations in these factors can influence the gravitational pull between objects. This leads us to consider not just the changes in mass but also the impact of distance, among other variables.
In this article, we will explore the various changes that can influence gravitational force, ultimately focusing on which change will always result in an increase in the gravitational force. By examining the fundamental principles of gravity, we will address common questions and misconceptions, providing clarity and insight into this essential topic. Whether you are a student, an enthusiast of physics, or simply curious about the forces that govern our universe, this exploration of gravitational force will deepen your understanding of one of nature's most important phenomena.
What is Gravitational Force?
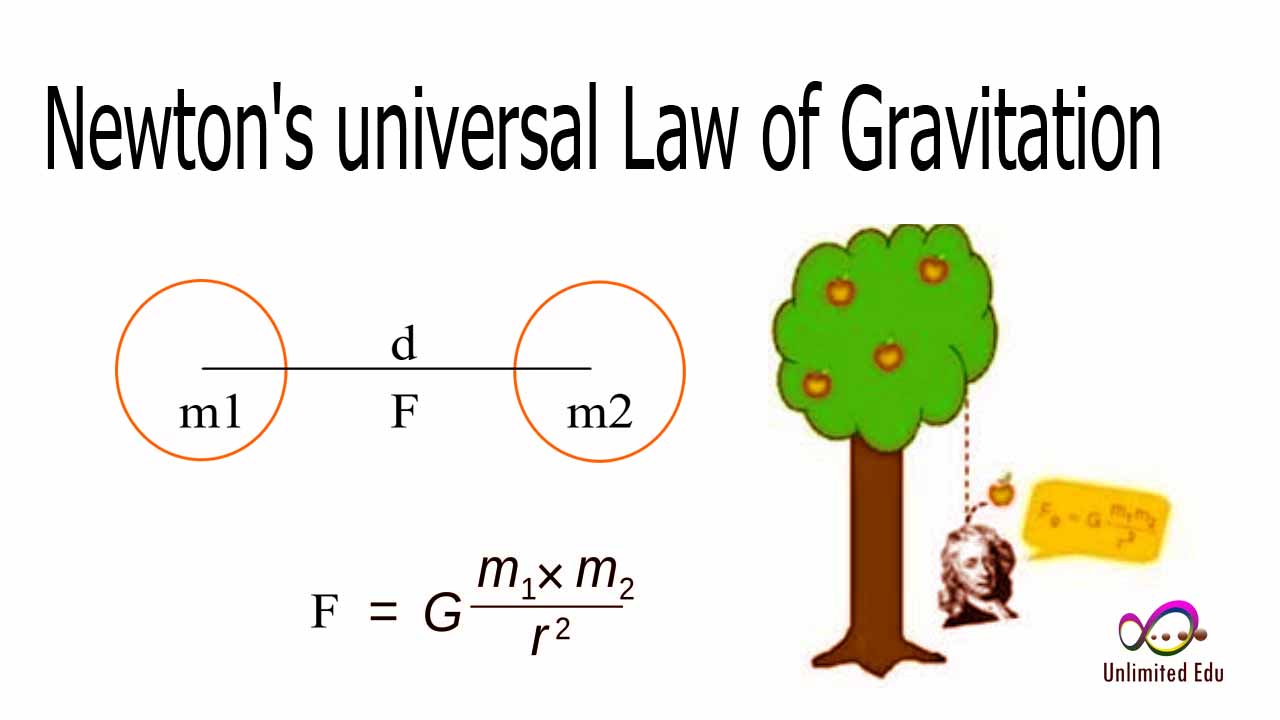
Gravitational force is defined as the attractive force that exists between any two objects with mass. This force is described by Sir Isaac Newton's law of universal gravitation, which states that every mass attracts every other mass in the universe. The strength of this force depends on two main factors: the masses of the objects involved and the distance between them.
How is Gravitational Force Calculated?
The formula for calculating gravitational force (F) between two masses (m1 and m2) is given by Newton's equation:
F = G * (m1 * m2) / r²
Where:
- G is the gravitational constant (approximately 6.674 × 10⁻¹¹ N(m/kg)²),
- m1 and m2 are the masses of the two objects, and
- r is the distance between the centers of the two masses.
Which Change Will Always Result in an Increase in the Gravitational Force?
The key factor that will always lead to an increase in gravitational force is an increase in the mass of one or both objects. According to Newton's law of universal gravitation, gravitational force is directly proportional to the product of the masses of the two objects. Therefore, if you double the mass of either object, the gravitational force will also double.
Can Distance Affect Gravitational Force?
Yes, distance plays a crucial role in the strength of gravitational force. The gravitational force decreases with the square of the distance between two objects. This means that as the distance increases, the gravitational attraction decreases significantly. In practical terms, this explains why we feel less gravitational pull from distant celestial bodies compared to those that are nearby.
What Are Other Factors That Influence Gravitational Force?
In addition to mass and distance, other factors can influence gravitational force, albeit not in the same consistent manner. These factors include:
- Shape and Density: The distribution of mass within an object can affect gravitational interactions.
- Rotation: The rotation of celestial bodies can create centrifugal forces that counteract gravitational pull.
- Gravitational Anomalies: Local variations in the Earth's density can lead to slight changes in gravitational force experienced in different locations.
Is Gravitational Force the Same Everywhere?
No, gravitational force is not uniform across the Earth or the universe. Variations in mass distribution, altitude, and local geological formations can lead to differences in gravitational pull. For instance, a person standing at sea level experiences a slightly stronger gravitational pull than someone at the top of a mountain due to the increased distance from the planet's center.
How Do Scientists Measure Gravitational Force?
Scientists utilize several methods to measure gravitational force, including:
- Gravimeters: Devices that measure gravitational acceleration with high precision.
- Satellite Observations: Data from satellites can help scientists calculate variations in gravitational forces.
- Free-Fall Experiments: Observing the acceleration of freely falling objects can provide insights into local gravitational forces.
What Are the Implications of Gravitational Force in Space Exploration?
Understanding gravitational force is essential for successful space exploration. It influences spacecraft trajectories, the behavior of satellites, and the feasibility of landing on different celestial bodies. Engineers and scientists must take gravitational factors into account when designing missions to ensure that they achieve their objectives safely and effectively.
Conclusion: What Have We Learned About Gravitational Force?
In conclusion, we have explored essential aspects of gravitational force, focusing on which change will always result in an increase in the gravitational force. Through our examination of mass, distance, and other influencing factors, we can appreciate the complex interactions that govern gravity. The relationship between mass and gravitational force is both straightforward and profound, reminding us of the fundamental principles that shape our universe. Understanding these principles not only enriches our knowledge of physics but also enhances our appreciation for the incredible forces at play in the cosmos.
You Might Also Like
Elia's Journey: Riding To The Beach At A Constant SpeedIn The Wake Of Desolation: The Tale Of A Half Depopulated Realm
How The Financial System Protects You: Understanding The Mechanisms Of Risk Minimization
Unraveling Complexity: The Nature Of Things That Are Difficult To Understand
Exploring The Evolution Of Continents Over Time
Article Recommendations