The universe is a vast expanse that is governed by intricate physical laws, particularly those relating to the masses of objects and the distances that separate them. Understanding these relationships not only enhances our knowledge of the cosmos but also provides valuable insights into everyday phenomena. The concept of gravitational force, which is fundamentally influenced by the masses of the objects involved and the distances between them, forms the backbone of celestial mechanics and physics.
When we talk about the masses of objects and increasing the distance between the objects, we delve into the realm of gravitational interactions. Every object with mass exerts a gravitational pull on every other mass. This force is influenced by two key factors: the amount of mass each object possesses and the distance that separates them. As we explore this topic, we will uncover how these elements interact in both theoretical and practical scenarios.
From the minute particles that make up our bodies to the celestial bodies scattered throughout the universe, the principles governing masses and distance are omnipresent. Not only does this understanding apply to physicists and astronomers, but it also resonates with anyone curious about the natural world. In this article, we will delve deeper into the relationship between the masses of objects and increasing the distance between them, unraveling the mysteries of gravitational forces and their implications.
What is the Gravitational Force?
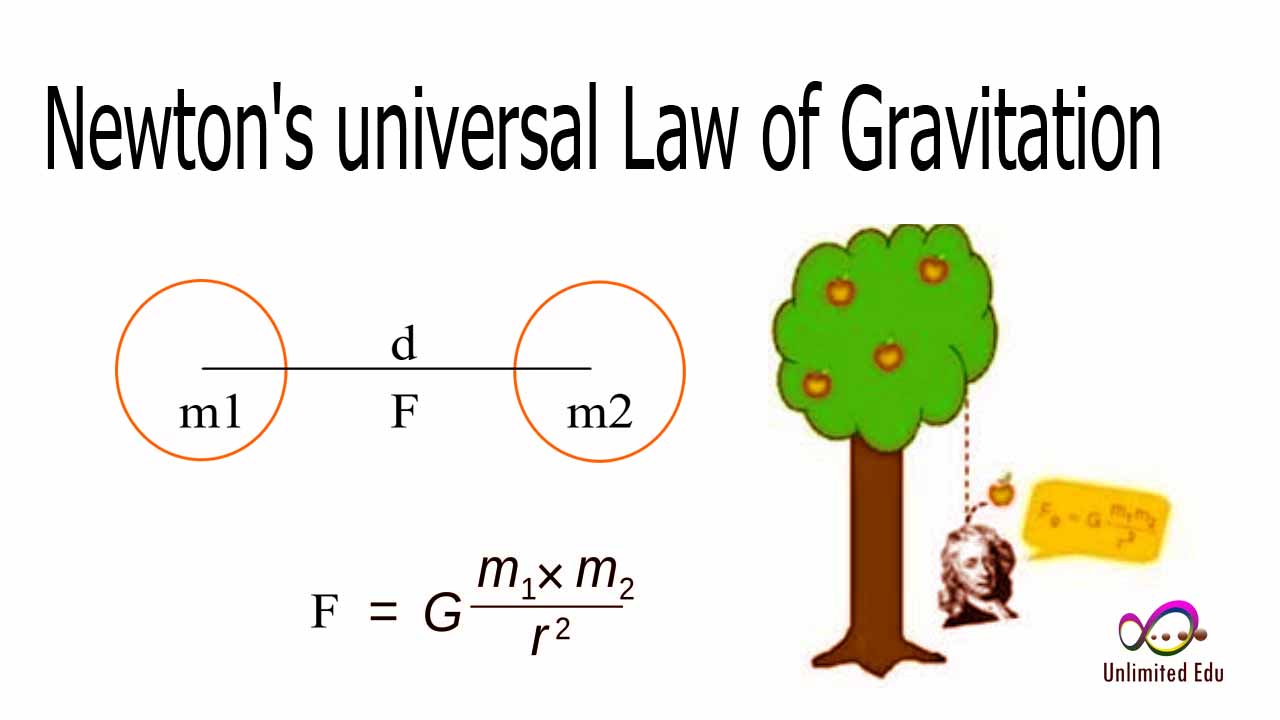
The gravitational force is a fundamental interaction in nature, responsible for the attraction between masses. It is described by Isaac Newton's law of universal gravitation, which states that every mass attracts every other mass with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. This relationship can be expressed mathematically as:
- F = G * (m1 * m2) / r^2
Where: - F is the gravitational force between the two masses, - G is the gravitational constant, - m1 and m2 are the masses of the objects, and - r is the distance between their centers.
How Do Masses Affect Gravitational Attraction?
The masses of objects play a crucial role in determining the strength of the gravitational force. Larger masses exert a stronger gravitational pull compared to smaller masses. For example, the Earth, with its significant mass, has a powerful gravitational force that keeps us grounded. In contrast, an ant, with its minuscule mass, exerts a negligible gravitational force on the Earth.
Why Does Distance Matter in Gravitational Interactions?
Distance is another vital factor in gravitational interactions. The further apart two objects are, the weaker the gravitational force between them. This inverse square relationship means that even a slight increase in distance can lead to a significant decrease in gravitational attraction. For example, if you were to move a football away from the Earth, the gravitational pull it experiences would diminish as the distance increases.
What Happens When Objects Move Further Apart?
As objects increase their distance from one another, the gravitational force diminishes. This principle can be observed in various scenarios, from celestial mechanics to everyday life. For instance, the gravitational pull of the moon affects the tides on Earth, but as the moon moves further away, its influence diminishes.
Can We Measure the Effects of Distance on Gravity?
Yes, scientists can measure the effects of distance on gravity through experiments and observations. One common method involves using pendulums or torsion balances to detect changes in gravitational force as objects are moved apart. These experiments help to confirm the predictions made by Newton's law of universal gravitation.
How Do Masses of Objects and Distance Influence Space Exploration?
The relationship between masses and distance is crucial for space exploration. When launching spacecraft, engineers must calculate the gravitational forces at play, as well as the distances involved. These calculations ensure that spacecraft can escape Earth’s gravitational pull and navigate through space effectively.
What Are Real-World Applications of These Principles?
The principles of masses of objects and increasing the distance between them have numerous real-world applications. Here are a few notable examples:
- Satellite Orbits: Understanding gravitational forces allows scientists to place satellites in stable orbits around Earth.
- Space Missions: Calculations regarding mass and distance are essential for planning missions to other planets, such as Mars.
- Engineering Structures: Engineers consider gravitational forces when designing structures to ensure their stability.
What Is the Future of Gravitational Research?
The study of gravitational forces and their relationship with mass and distance continues to evolve. Researchers are exploring concepts such as gravitational waves and dark matter, which may further illuminate our understanding of the universe. As technology advances, we can expect new discoveries that challenge our current perceptions of gravity.
Conclusion: Why Understanding Masses and Distance Matters
In conclusion, the interplay between the masses of objects and the increasing distance between them is a fundamental aspect of physics that affects everything from our daily lives to the exploration of outer space. By grasping these concepts, we not only satisfy our curiosity about the natural world but also pave the way for advancements in technology and exploration. The gravitational force, influenced by mass and distance, governs the universe, shaping the very fabric of reality we experience every day.
You Might Also Like
Understanding Conflict: Which Sentence Best Describes A Conflict?Embracing Growth: The Change That Always Leads To Increase
Exploring The Shadows: Young Goodman Brown's Secret Meeting
Driving Change: A Positive Incentive To Encourage Motorists
Understanding The Dynamics Of Gravitational Force: What Factors Contribute?
Article Recommendations