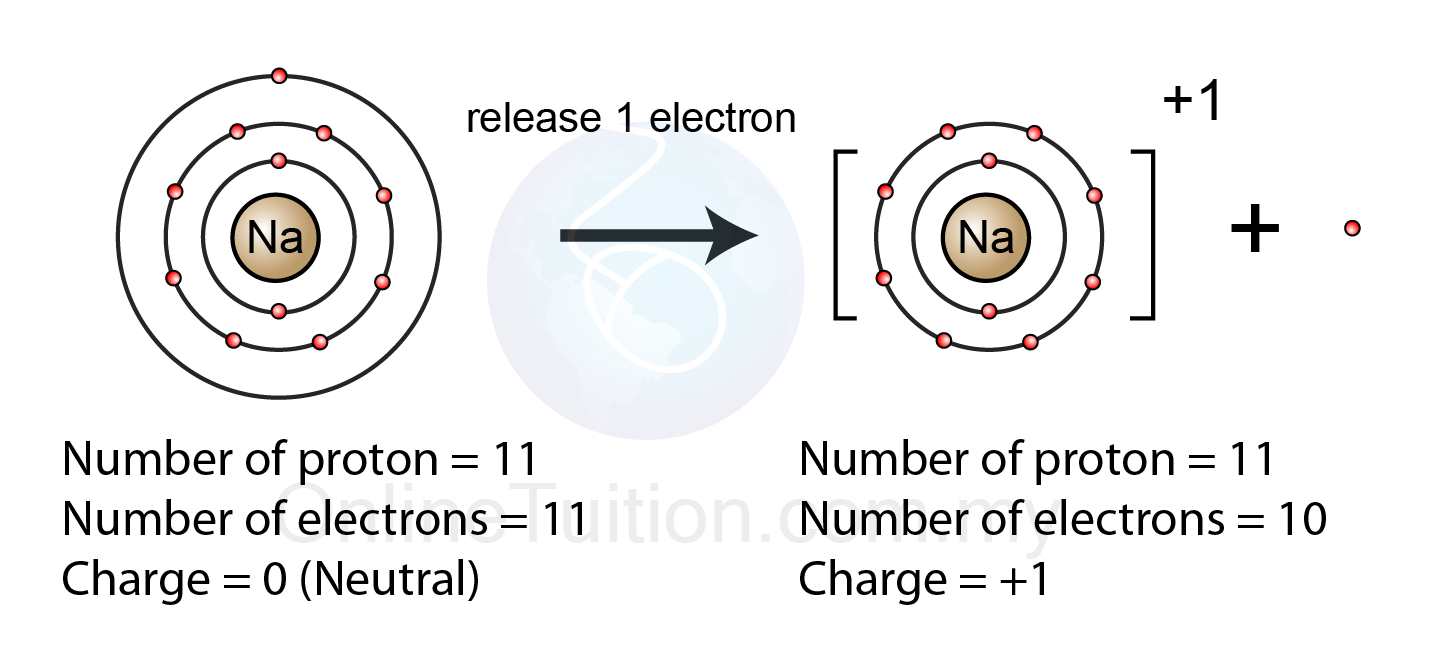
In the world of chemistry, understanding the behavior of elements is crucial for grasping the fundamental principles of matter. One key aspect of this behavior is the formation of ions, specifically positive ions or cations. These charged particles play a vital role in various chemical reactions and processes. The formation of positive ions occurs when an atom loses one or more electrons, resulting in a net positive charge. But which elements are most likely to form these positive ions, and what factors influence this phenomenon?
Throughout this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of positive ions, examining the elements that are prone to this behavior. From alkali metals to transition metals, each group of elements exhibits unique characteristics that dictate their tendency to form cations. Additionally, we will explore the significance of these ions in various applications, including their role in biological systems and industrial processes.
By gaining a deeper understanding of what elements form positive ions, we can appreciate the intricate relationships between atomic structure, electron configuration, and chemical reactivity. So, let us embark on this journey to uncover the elements that contribute to the formation of positive ions and their implications in the realm of chemistry.
What Elements Are Known to Form Positive Ions?
Positive ions, or cations, are formed by various elements, primarily metals. The following groups of elements are particularly known for their ability to form positive ions:
- Alkali Metals: These are found in Group 1 of the periodic table and include lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K), rubidium (Rb), cesium (Cs), and francium (Fr). They readily lose one electron to form +1 cations.
- Alkaline Earth Metals: Located in Group 2, these metals such as magnesium (Mg) and calcium (Ca) typically lose two electrons, forming +2 cations.
- Transition Metals: Found in the center of the periodic table, transition metals like iron (Fe), copper (Cu), and zinc (Zn) can form cations with varying charges, commonly +1, +2, or +3.
- Post-Transition Metals: Elements such as aluminum (Al) and tin (Sn) also tend to lose electrons, forming positive ions.
How Do Electron Configurations Influence Ion Formation?
The electron configuration of an element plays a pivotal role in its ability to form positive ions. Elements with fewer electrons in their outer shell are more likely to lose those electrons and achieve a stable electron configuration. For instance:
- Alkali Metals: With one electron in their outermost shell, alkali metals easily lose that electron to reach a noble gas configuration.
- Alkaline Earth Metals: These elements have two electrons in their outer shell. Losing both electrons allows them to achieve stability.
- Transition Metals: These elements have complex electron configurations, allowing them to lose varying numbers of electrons and form multiple positive ions.
What Are the Properties of Positive Ions?
Positive ions exhibit several key properties that influence their behavior in chemical reactions:
- Charge: As cations, positive ions carry a net positive charge, which affects their interactions with other charged particles.
- Size: Cations are generally smaller than their neutral counterparts due to the loss of electrons, leading to increased nuclear attraction on the remaining electrons.
- Solubility: Many positive ions are soluble in water, which is crucial for their role in biological systems and industrial applications.
Why Are Positive Ions Important in Chemistry?
Positive ions play a crucial role in various chemical processes and applications, including:
- Electrolytes: Cations are essential for conducting electricity in solutions, making them vital in biological systems and electrochemical processes.
- Reactivity: The presence of positive ions influences the reactivity of compounds, affecting how substances interact and form new products.
- Biological Functions: Many biological processes depend on cations, such as sodium (Na+) and potassium (K+), which are crucial for nerve impulses and muscle contractions.
Which Elements Form Positive Ions in Biological Systems?
In biological systems, certain elements are particularly known for forming positive ions that are vital for life. These include:
- Sodium (Na+): Essential for maintaining osmotic balance and transmitting nerve impulses.
- Potassium (K+): Crucial for muscle function and maintaining cellular functions.
- Calcium (Ca2+): Important for bone health, muscle contraction, and neurotransmitter release.
How Do Positive Ions Contribute to Industrial Applications?
Positive ions also play a significant role in various industrial applications, including:
- Catalysis: Certain positive ions serve as catalysts in chemical reactions, enhancing the efficiency of processes.
- Electroplating: Cations are used in electroplating to deposit metal coatings onto surfaces, improving durability and appearance.
- Battery Technology: Positive ions are integral to the functioning of batteries, facilitating the flow of electricity and energy storage.
What Challenges Are Associated with Positive Ions?
While positive ions are essential in many applications, there are challenges associated with their behavior:
- Corrosion: Certain positive ions can contribute to the corrosion of metals, posing challenges in industries such as construction and manufacturing.
- Toxicity: Some cations can be toxic to living organisms, requiring careful management in environmental and health contexts.
- Complexity in Reactions: The presence of multiple cations in a solution can lead to complex interactions, complicating chemical processes.
What Future Research Opportunities Exist in the Study of Positive Ions?
The study of positive ions presents numerous research opportunities, particularly in areas such as:
- New Materials: Investigating the properties of new cationic materials for applications in electronics and energy storage.
- Environmental Science: Understanding the behavior of positive ions in environmental systems to address pollution and remediation strategies.
- Biochemistry: Exploring the role of cations in biological processes and their potential therapeutic applications.
Conclusion: What Elements Form Positive Ions?
In summary, understanding what elements form positive ions is essential for grasping the complexities of chemistry and its applications in various fields. From alkali metals to transition metals, the ability of elements to lose electrons and form cations influences their reactivity, properties, and significance in both biological systems and industrial processes. Continued research in this area promises to yield new insights and innovations, further enhancing our understanding of the vital role positive ions play in our world.
You Might Also Like
When Cows Get Creative: The Sign, The Fence, And The FunUnveiling The Mystique Of Bulging Or Staring Eyes With Light Iris
Inspiring Stories Of Those Who Were Either Immigrants Themselves Or The Children Of Immigrants
Exploring Characters: Are They Dynamic Or Static?
Unlocking The Mystery Of Earnings: How To Solve For More After Earning $25
Article Recommendations