Understanding the intricate relationship between mass and gravitational force is a fundamental aspect of physics that often intrigues both students and seasoned scientists alike. When we talk about the gravitational pull between two objects, one of the key elements at play is the mass of each object involved in this interaction. The relationship is not merely theoretical; it has profound implications across various fields, from engineering to astrophysics. In this article, we will delve into how increasing the masses of the objects affects their gravitational attraction and explore the underlying principles that govern this phenomenon.
The gravitational force between two objects is a central topic in physics, governed by Newton's law of universal gravitation. According to this law, the gravitational force is directly proportional to the product of the masses of the two objects and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centers. This relationship can lead to fascinating discussions about what happens when the masses of these objects are altered. What if we were to increase the masses? How would that impact the gravitational dynamics?
As we navigate through the complexities of gravitational interactions, we will pose critical questions that challenge our understanding of mass and distance. We aim to provide insights into the various scenarios that arise when mass is adjusted, and the gravitational implications of these changes. Join us as we unravel the mysteries of gravitational forces and their dependence on mass.
What is the Relationship Between Mass and Gravitational Force?
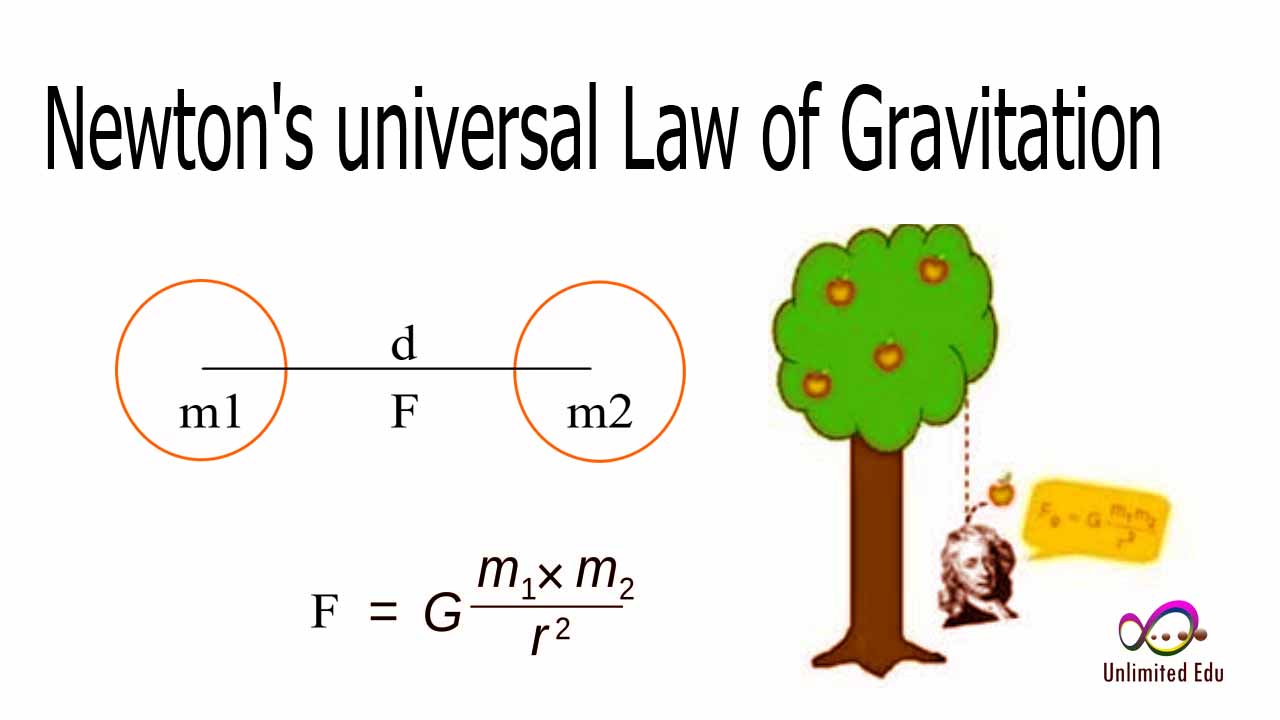
The relationship between mass and gravitational force can be best understood through Newton's law of universal gravitation, which states:
- The gravitational force (F) between two objects is given by the formula: F = G * (m1 * m2) / r²
- Where G is the gravitational constant, m1 and m2 are the masses of the two objects, and r is the distance between their centers.
As per this formula, if either mass increases, the gravitational force between the two objects will also increase, provided the distance remains constant. This principle is not only a theoretical construct; it has practical implications in understanding celestial mechanics, satellite orbits, and much more.
How Does Increasing the Mass of One Object Affect the Other?
When we consider increasing the mass of one object, the effects can be quite significant. For example, if we were to double the mass of one object while keeping the other constant, the gravitational force would also double. This can lead to various observable phenomena, especially in astrophysical contexts.
Can We Observe These Changes in Everyday Life?
Indeed! While we may not always notice the gravitational effects in our daily lives, they are present. For instance, the weight of an object on Earth is a direct result of the Earth's mass and its distance from the object. If Earth's mass were to increase significantly, we would experience an increase in weight due to the stronger gravitational pull.
What Happens When Both Masses are Increased?
When both masses are increased, the gravitational interaction becomes even more pronounced. For example, if both masses are tripled, the gravitational force is increased by a factor of nine, given that the distance remains unchanged. This principle can be visualized using simple experiments with weights and pulleys, demonstrating how mass directly influences gravitational force.
How Does Distance Factor Into Gravitational Changes?
Distance plays a crucial role in gravitational interactions. As per the inverse square law, even a slight increase in distance can lead to a significant decrease in gravitational force. Therefore, while increasing mass amplifies the gravitational force, the distance must also be considered to fully understand the dynamics at play.
What Real-World Applications Can We Find?
The principles of mass and gravitational force are applied in various fields:
- Aerospace Engineering: Understanding gravitational forces is essential for satellite launches and space missions.
- Earth Sciences: Gravitational studies help in understanding tectonic movements and Earth's structure.
- Physics Research: Experiments in particle physics often rely on gravitational concepts to explore fundamental forces.
How Do Scientists Measure Gravitational Forces?
Scientists utilize a variety of methods to measure gravitational forces, ranging from pendulum experiments to advanced satellite technology. These measurements not only confirm theoretical predictions but also provide data for further study and experimentation.
Can Technology Alter Gravitational Effects?
While technology cannot change the fundamental laws of gravity, it can help manipulate conditions to study gravitational effects. For example, scientists use powerful magnets or vacuum environments to minimize external forces, allowing them to focus solely on gravitational interactions.
In Summary: What Have We Learned About Mass and Gravity?
Understanding the relationship between mass and gravitational force is crucial in both theoretical and practical realms. Between two objects? Increasing the masses of the objects and increasing their gravitational pull is a fundamental principle that has applications in numerous scientific fields. By exploring these dynamics, we not only enhance our knowledge of physics but also improve our technological advancements and our understanding of the universe.
You Might Also Like
Finding The Equivalent (or A Close Equivalent) Of The Words And Meanings Expressed ByUnderstanding The Tax Implications Of Straight-Line Depreciation At Year 10
Understanding The Facility And Business Dynamics: Can Gwyn Rescind The Deal?
Soaring High: The Journey Of My Kite Fly
Unveiling The Mystery Of Reeleak.con: What You Need To Know
Article Recommendations
- Dana Kinduryte The Rising Star In The Financial World
- Comprehensive Guide To Rosanna Arquettes Film Career
- Low Taper Fade