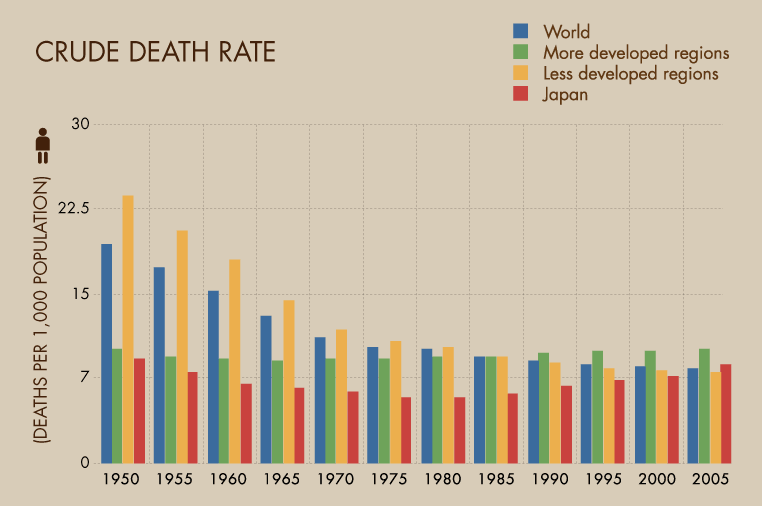
The crude death rate (CDR) is a critical demographic measure that reflects the mortality level of a population in a specific time frame. This metric is expressed as the number of deaths per 1,000 individuals in a given year and serves as an essential tool for public health officials, researchers, and policymakers. Understanding the crude death rate is crucial for assessing the overall health of a population and for identifying trends over time. The crude death rate not only highlights the immediate impact of health crises but also provides insight into the effectiveness of healthcare systems, social conditions, and economic stability. By examining variations in CDR, we can better grasp the underlying factors influencing mortality rates and work towards improving public health strategies.
As global health challenges continue to evolve, the crude death rate remains a fundamental statistic that can guide intervention efforts. It helps to inform us about the effects of diseases, natural disasters, and other demographic shifts. Moreover, the crude death rate can also serve as a benchmark for comparing different countries or regions, aiding in the identification of areas in need of support or improvement.
In this article, we will explore the concept of crude death rate in depth. We will answer several key questions, including what the crude death rate is, how it is calculated, and what factors influence this important public health indicator. Additionally, we will examine the significance of crude death rate trends and their implications for society at large.
What is Crude Death Rate?
The crude death rate is defined as the total number of deaths occurring in a population over a specified period, typically one year, divided by the total population size, then multiplied by 1,000. This rate provides a standardized measure that allows for the comparison of mortality rates across different populations, regardless of their size.
How is Crude Death Rate Calculated?
The calculation of the crude death rate can be broken down into a simple formula:
- Crude Death Rate (CDR) = (Number of Deaths / Total Population) x 1,000
For example, if a country has 1,000 deaths in a year and a total population of 100,000, the crude death rate would be:
- CDR = (1,000 / 100,000) x 1,000 = 10 deaths per 1,000 population.
What Factors Influence Crude Death Rate?
Several factors can affect the crude death rate, including:
- Age structure: A population with a higher proportion of elderly individuals typically has a higher crude death rate.
- Health care access: Regions with better healthcare facilities tend to have lower crude death rates.
- Socioeconomic status: Higher levels of poverty and lower education can lead to increased mortality rates.
- Environmental factors: Natural disasters, pollution, and living conditions can all impact mortality rates.
Why is Crude Death Rate Important?
The crude death rate serves as a vital indicator for public health assessments and demographic studies. Understanding the CDR can help in:
- Identifying public health crises: A sudden spike in crude death rate can signal an outbreak of disease or other health emergencies.
- Guiding health policy: Policymakers can use CDR data to allocate resources and implement health interventions where they are most needed.
- Tracking population changes: Over time, trends in crude death rate can reveal shifts in population health and longevity.
How Does Crude Death Rate Compare to Other Mortality Rates?
While the crude death rate is a useful measure, it is essential to differentiate it from other mortality rates, such as:
- Age-specific death rate: This measures the number of deaths within a specific age group, providing a more detailed view of mortality.
- Cause-specific death rate: This focuses on deaths resulting from particular causes, allowing for targeted public health responses.
- Infant mortality rate: This measures the number of deaths of infants under one year of age, providing insight into maternal and child health.
What Trends Can Be Observed in Crude Death Rate Over Time?
Observing trends in the crude death rate can yield valuable insights into the health of a population. Common trends include:
- Declining crude death rates: This often indicates improvements in healthcare, living conditions, and overall public health.
- Rising crude death rates: This may signal emerging health crises, such as disease outbreaks or insufficient healthcare resources.
- Regional variations: Different regions may experience varying trends due to socioeconomic factors, healthcare access, and environmental conditions.
Conclusion: The Significance of Crude Death Rate in Public Health
In summary, the crude death rate is a fundamental metric in understanding population health and mortality trends. By providing a standardized measure, the crude death rate enables researchers and policymakers to make informed decisions that can ultimately improve health outcomes. As we continue to face global health challenges, monitoring the crude death rate will remain essential in our efforts to enhance public health and ensure the well-being of communities around the world.
You Might Also Like
Cindy Busby: The Rising Star Of The ScreenExploring The Life And Achievements Of Jordan Harrelson
Exploring The Wealth Of Patrick Kluivert: His Net Worth And More
Unveiling The Intricate Web Of Giancarlo Esposito Relationships
Mark Sloan: The Charismatic Surgeon Who Captivated Hearts
Article Recommendations